A vulnerability assessment involves identifying, classifying, and prioritizing security vulnerabilities within an IT infrastructure. This comprehensive evaluation determines if an IT system is susceptible to known vulnerabilities. It also assigns severity levels to these vulnerabilities and recommends mitigation steps as necessary.
Hours delivered back to the business
SOX compliance in Settlement process automation
Success rate of bot case completion
For functional release of OBT, RTS and OGS
Vulnerability assessment is a standard security procedure, that offers a detailed overview of the security risks an organization might encounter. This enables better protection of their IT systems and sensitive data against cyber threats. Vulnerabilities can exist in both third-party applications and internally developed software. Once identified, many of these flaws can be easily rectified.
Importance of Vulnerability Assessment
Vulnerability assessment is crucial as it identifies security weaknesses in your environment and offers guidance on how to address these issues before exploitation. This process enhances the understanding of IT infrastructure, security flaws, and overall risk. It also significantly improves information and application security standards while reducing the chances of attackers gaining unauthorized access to your organization.
Types of Vulnerability Assessment
Understanding the different types of vulnerability assessments is crucial for identifying and addressing various security risks within your IT infrastructure. Below are the types of vulnerability assessment.

Network-Based Vulnerability Assessment
A network-based vulnerability assessment targets vulnerabilities present in network devices like routers, switches, firewalls, and other infrastructure components. Its primary objective is to uncover weaknesses in the network that attackers might exploit to gain unauthorized access, compromise data, or execute malicious activities.
This assessment method utilizes specialized software tools and techniques designed to scan the network comprehensively. These tools employ diverse methods such as port scanning, vulnerability scanning, password cracking, and network mapping to identify potential vulnerabilities and assess the overall security posture of the network.
Application-Based Vulnerability Assessment
An application vulnerability assessment involves evaluating security weaknesses in software applications (Layer 7), encompassing websites, mobile apps, and APIs. The goal is to determine if these applications are vulnerable to known security issues and to classify the severity or criticality of each vulnerability, providing recommendations for remediation or mitigation as necessary.
These assessments typically include testing applications for prevalent vulnerabilities like SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and other vulnerabilities listed in the OWASP Top 10. They employ a combination of automated tools and manual testing methods to thoroughly assess the application’s security posture.
API-Based Vulnerability Assessment
An API vulnerability assessment aims to discover and address APIs’ inherent security risks. This evaluation process identifies vulnerabilities and weaknesses across the API’s design, implementation, and deployment phases. The objective is to enhance the API’s security, reliability, and resilience against potential attacks.
Host-Based Vulnerability Assessment
A host-based vulnerability assessment targets vulnerabilities within individual host systems, encompassing servers, workstations, and laptops.
These assessments typically entail scanning the host system to uncover known vulnerabilities, such as outdated software or missing security patches. Host-based vulnerability assessments employ both automated and manual methodologies.
Wireless Vulnerability Assessment
A wireless network vulnerability assessment is aimed at uncovering vulnerabilities in wireless networks, including Wi-Fi networks. These assessments involve testing the wireless network for prevalent security weaknesses, such as inadequate encryption, default passwords, and rogue access points.
Cloud-Based Vulnerability Assessment
A cloud-based vulnerability assessment aims to uncover vulnerabilities within cloud infrastructure and services, such as Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Microsoft Azure. These assessments involve scanning the cloud infrastructure for known vulnerabilities and evaluating the security posture of cloud applications and services.
Methodology of Vulnerability Assessment
Below is the process for conducting a vulnerability assessment for an organization:
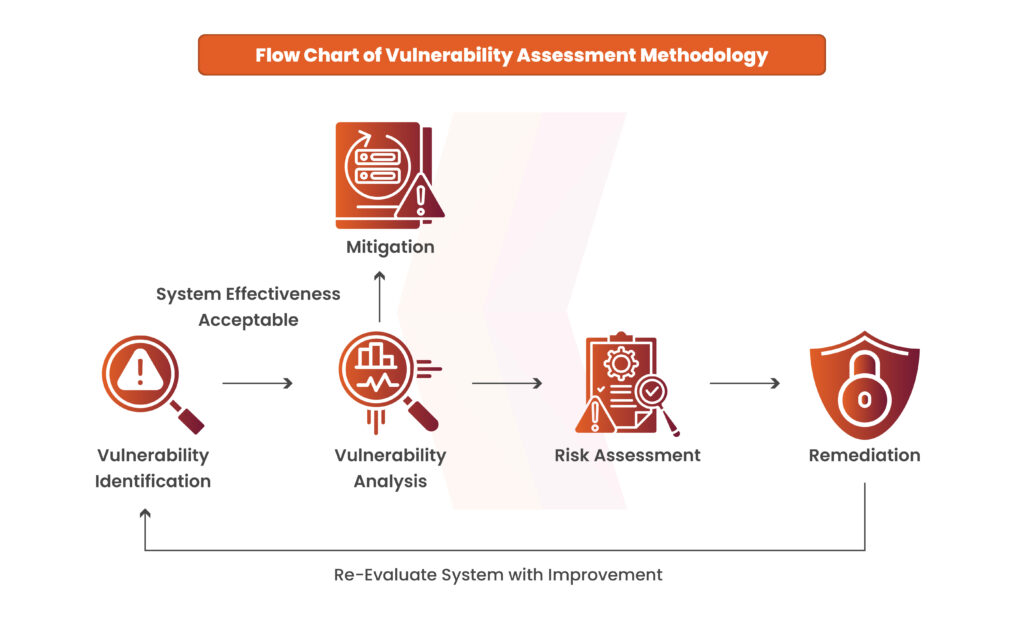
Vulnerability Identification
Vulnerability identification involves discovering and compiling a comprehensive list of vulnerabilities within your IT infrastructure. This process typically utilizes a combination of automated vulnerability scanning and manual penetration testing. A vulnerability scanner assesses systems, networks, or web applications for known vulnerabilities, such as those listed on the Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE).
The assessment is performed through 2 types of scans:
- Authenticated Scans
This type of scan assesses networked resources using remote administrative protocols and authenticates with system credentials. Authenticated scans offer the advantage of accessing low-level data, such as specific services, configuration details, and accurate information about operating systems, installed software, configuration issues, access control, security controls, and patch management.
- Unauthenticated Scans
Avoid granting access to networked resources, as this can lead to false positives and unreliable information about operating systems and installed software. Such scans are typically used by cyber attackers and IT security analysts to assess the security posture of externally facing assets, third-party vendors, and to identify potential data leaks.
Vulnerability Assessment approach includes identifying and classifying vulnerabilities in a system, network, or application. We Use automated scanners and tools to find potential security issues. It might include manual verification to eliminate false positives. We also provide recommendations for remediation of the vulnerabilities.
Vulnerability Analysis
After identifying vulnerabilities, it’s essential to pinpoint which components are responsible for each one and uncover the root cause of the security weaknesses. For example, an outdated version of an open-source library might be the root cause.
In such cases, remediation is straightforward: upgrade the library. However, solutions aren’t always this simple. Organizations often need to run each vulnerability through a security assessment process that classifies the severity, identifies possible solutions, and determines whether to accept, remediate, or mitigate the risk based on the organization’s risk management strategy.
Risk Assessment
The goal of this step is to prioritize vulnerabilities. This typically involves utilizing a vulnerability assessment tool that assigns a rank or severity level to each identified vulnerability.
Remediation
Vulnerability remediation involves addressing security issues identified as unacceptable in the risk assessment process. This usually requires collaboration between development, operations, compliance, risk management, and security teams to determine a cost-effective solution for each vulnerability.
Many vulnerability management systems offer recommended remediation techniques for common vulnerabilities, which can range from installing readily available security patches to replacing hardware.
Mitigation
Not all vulnerabilities can be fully remediated, which is where mitigation comes in. Mitigation focuses on lowering the likelihood of exploitation or minimizing the impact if an exploit occurs.
Mitigation steps vary depending on risk tolerance and budget but often include:
- Implementing new security controls
- Replacing hardware or software
- Encryption
- Vendor risk management
- Attack surface management
- Continuous security monitoring





